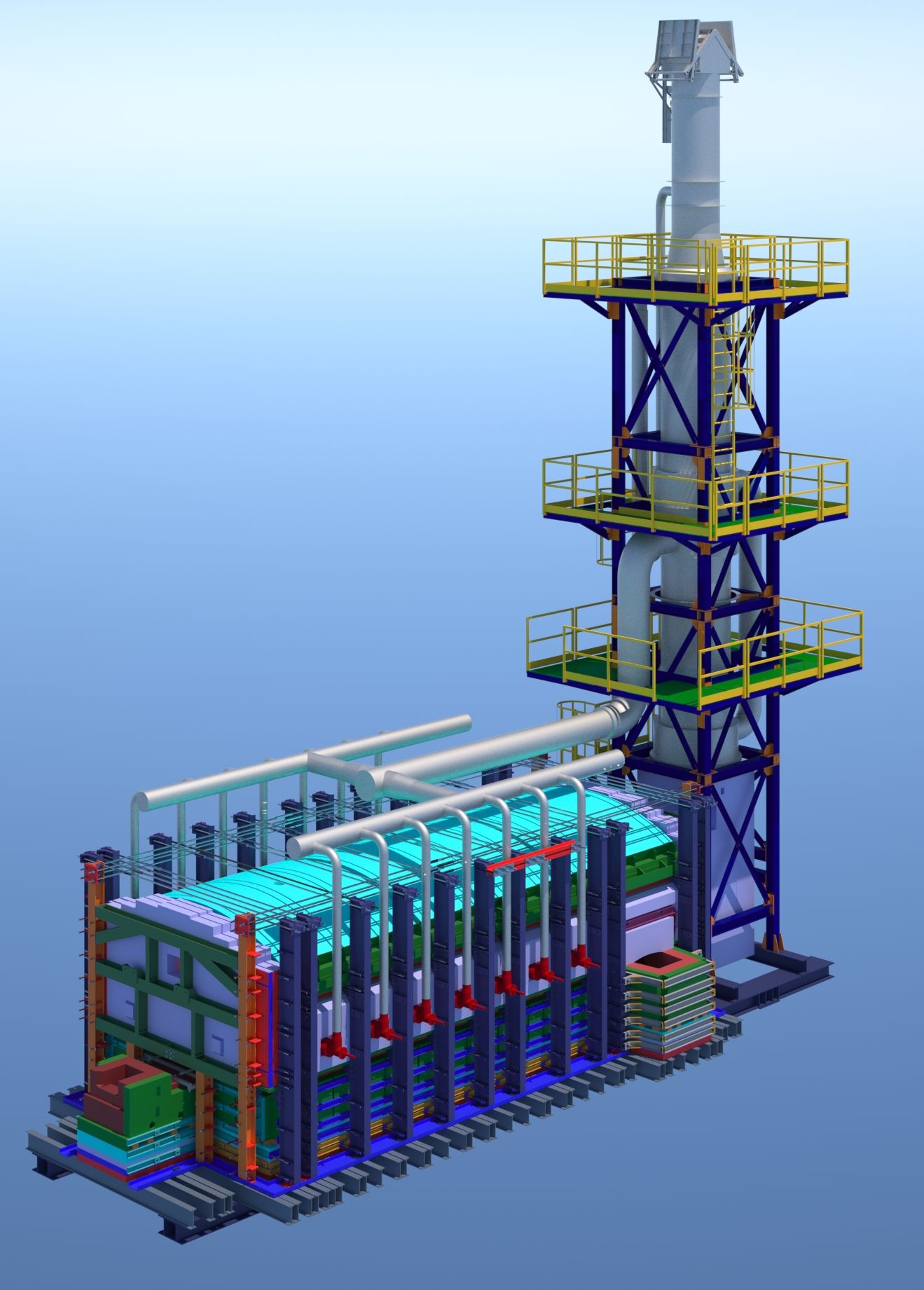
In recuperative type furnaces, the combustion air is preheated inside a steel recuperator where the high residual energy of the hot gases is given to the combustion air
The heat exchange process is continuous while and the air and gas flow in parallel separated by a thin metallic wall.
Depending on the technology of the recuperator the hot air can be heated from min 500-550°C (conventional double shell type systems) to max 800 – 850°C (tube bundle type systems).
The limit of hot air temperature is directly connected to the steel mechanical resistance which cannot reach values comparable with refractory materials as the regenerative furnace.
The heating burners are installed in a cross fired configuration which contributes to generating the optimal temperature profile in the glass tank at any furnace load.
The recuperative furnace is mostly used in small and medium scale production plants and is popular in tableware glass.
The main features of a recuperative furnace are:
- Suitable for small-medium size production (from 10 up 100 tpd)
- Low investment in infrastructures
- Low emissions
- Reliable technology
- Excellent flexibility to pull variation
- Easy operation
- Extended lifetime
Type of glass:
- Soda-lime
- Crystalline
- Light borosilicate
- Sodium silicate
Fields of application:
- Container glass
- Tableware
- Kitchenware
- Pharmaceutical
Related arguments:
- Natural Gas heating systems
- HFO heating systems
- Backup systems
- Recuperative burners
- Screw type batch chargers
- Scoop type batch chargers
- Oscillating tray type batch chargers
- Glass level
- Bubbling system
- Electric booster
- Tank and throat cooling
- Control cabinets
- SCADA supervision systems
- Jet Air Damper
- Double shell recuperators
- Tube bundle type recuperators